Have you ever wondered how much time your support agents spend searching for the information they need to assist customers effectively? Studies reveal that support agents spend around 20% of their workweek searching for answers or seeking help from colleagues. This inefficiency not only hampers productivity but also affects customer satisfaction.
Imagine a scenario where your support agents can provide instant answers to customer queries, eliminating delays. Sounds ideal, doesn’t it? This is where an internal knowledge base becomes a game-changer. By centralizing information, it streamlines processes and equips agents to handle queries efficiently and confidently.
In this guide, we’ll explore what an internal knowledge base is, the essential features it should have, and highlight some top tools that can help you build and maintain an effective knowledge repository.
What is a knowledge base tool?
A knowledge base is essentially a library of information related to your product or service. It can take two forms:
- External knowledge base: A resource that customers can access to resolve their queries independently.
- Internal knowledge base: Designed specifically for employees, particularly support agents. It centralizes critical information such as product guides, troubleshooting tips, policies, and procedures.
- Fact: 67% of consumers prefer using self-service portals over interacting with customer service representatives for simple issues.
Source: Forrester
Support agents often spend more than 25% of their work time searching for information. This translates to roughly 500 hours a year per agent! An internal knowledge base software significantly reduces this time by making information readily available in one centralized location.
Understanding the importance of an internal knowledge base
A lot of companies do not have a central repository to maintain information. Vital information is scattered across various platforms—emails, printed documents, shared folders, or random files. For a support agent dealing with an impatient customer, searching through such disorganized data is not only frustrating but also detrimental to the customer experience.
An internal knowledge base resolves this problem by acting as a centralized hub to store, manage, and share information efficiently. Here are a few reasons why you need it?
- Improves collaboration between teams
- Reduces the time spent in finding the solution by digging through emails or shared files
- Makes employee training easier
- Improves agent productivity and transparency
- Ensures consistency across departments
1. Improves team collaboration
An internal knowledge base software encourages teams to work together by providing a shared platform for storing and accessing information. This eliminates silos, ensuring everyone has access to the same up-to-date resources.
2. Reduces time spent searching for information
Instead of digging through endless email threads or shared folders, agents can find what they need instantly. This saves valuable time, allowing them to focus on resolving customer issues quickly and effectively.
3. Simplifies employee training
Onboarding new employees or training existing ones becomes seamless when all necessary resources are available in one place. This ensures consistent and efficient knowledge transfer.
4. Boosts agent productivity
When support agents can find information effortlessly, they can focus on delivering good customer service. A well-structured knowledge base can significantly enhance agent productivity, efficiency and satisfaction.
5. Ensures consistency across departments
Customers expect consistent experiences across all touchpoints. An internal knowledge base software ensures that all employees have access to the same guidelines and information, providing uniformity in customer interactions.
For support agents who constantly face the same kind of problems an internal knowledge base is like a cherry on the cake.
Why do you need an internal knowledge base?
1. Simplified employee onboarding
Joining a new company can be overwhelming for employees. With internal knowledge management software, all essential resources such as company policies, product guides, and processes are readily available. New hires can independently find answers to their questions, reducing their reliance on colleagues and speeding up the onboarding process.
This is especially beneficial for growing support teams, ensuring each agent can hit the ground running with minimal disruption.
2. Easy training and retraining
Customer service processes evolve regularly, and keeping everyone in the loop is crucial. An internal knowledge management software simplifies this by providing updated training documents, checklists, and other resources in one place.
Version control ensures that employees can access the latest documents while still being able to refer to older versions if needed
3. Enhanced agent productivity
Customer expectations are always rising, and agents need to respond quickly. With a self-service knowledge base integrated into their workflow, agents can find answers instantly, saving time and improving productivity.
Bonus tip: Integrating the knowledge base with AI-powered tools and agent bots can further streamline information retrieval.
4. Consistency across departments
Regardless of the communication channel—whether it’s email, chat, or phone—customers expect the same level of service. An internal knowledge base ensures consistency by providing a single source of truth that all teams can rely on.
5. Streamlined collaboration
When an update is made to a knowledge base article, how do you ensure all team members are notified? Sending emails or relying on group chats can lead to missed updates.
An internal knowledge base simplifies collaboration by allowing team members to edit, review, and manage versions of articles within the platform itself. This ensures everyone stays informed without unnecessary clutter.
What information should a knowledge base include?
Now that we know a knowledge base helps to store, manage, and share information let’s explore the key types of information that should be included in a company knowledge base, along with examples of how it can be used effectively.
1. News and product updates
Keeping your team informed about product updates and company news is crucial for alignment and collaboration. A knowledge base can act as a one-stop platform for sharing such updates across the organization.
Examples of what to include:
- New feature launches
- Upcoming product announcements
- Process changes
- Service updates
2. Training materials
A well-structured knowledge base can simplify training for both new hires and existing employees. It can house all the resources necessary for onboarding, ongoing education, and skill development, making learning a seamless experience.
Examples of what to include:
- Onboarding guides
- Role-specific resources
- How-to guides and tutorials
3. FAQs and troubleshooting resources
Every organization encounters recurring questions or issues, whether from customers or employees. Including a section dedicated to frequently asked questions (FAQs) and troubleshooting can save time and improve productivity.
Examples of what to include:
- Common customer queries
- Troubleshooting steps
- Error resolution guides
4. Policies and procedures
A knowledge base is an ideal place to document company policies and procedures. This ensures that all employees can access this information when needed and helps maintain compliance and transparency.
Examples of what to include:
- HR policies
- Operational procedures
- Compliance guidelines
5. Customer insights and feedback
Your customer-facing teams often gather valuable insights and feedback from users. Storing this information in the knowledge base can help the entire organization better understand customer needs and preferences.
Examples of what to include:
- Customer personas
- Feedback summaries
- Case studies
6. Collaboration and project documentation
In today’s fast-paced work environments, teams often collaborate on complex projects. An internal knowledge base can store project-related information, making it accessible to all stakeholders.
Examples of what to include:
- Project timelines and updates
- Meeting notes
- Shared goals
7. Best practices and guidelines
A knowledge base is an excellent platform for storing best practices and guidelines that can enhance employee performance and decision-making.
Examples of what to include:
- Customer interaction tips
- Quality standards
- Productivity hacks
Features to include in an internal knowledge base
Creating a robust internal knowledge base requires a thoughtful selection of features that cater to both usability and functionality. Below are essential features that should be included, along with an explanation of how they contribute to building an efficient and user-friendly platform:
1. Categories and folders for organization
A well-structured knowledge base is key to easy navigation. By organizing content into categories and folders, you allow users to quickly locate the information they need. This helps employees find relevant articles without wading through unrelated content and categorization enhances the effectiveness of search filters and ensures the knowledge base remains manageable and organized.
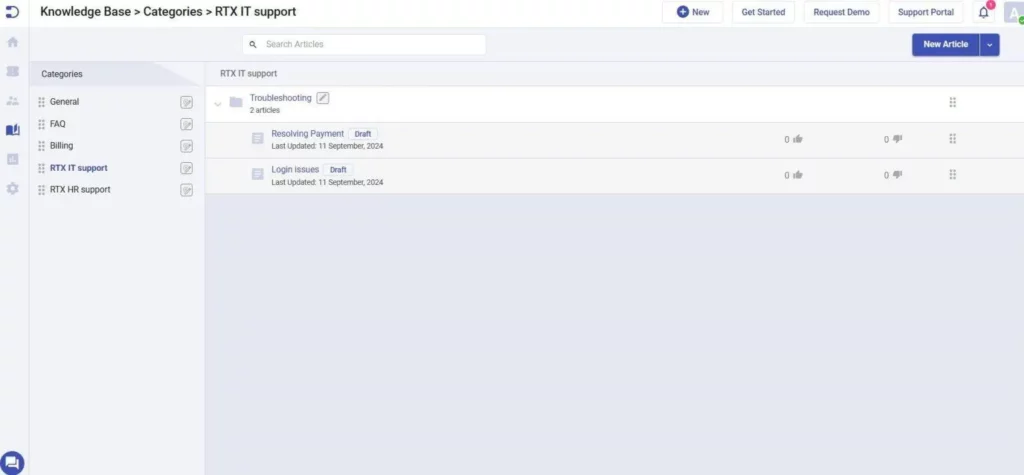
2. Article versioning
Article versioning ensures that every update to a document is tracked and managed effectively.
Features to include:
- Edit history: Keep a log of all changes made to an article.
- Restore previous versions: Allow users to revert to earlier versions if needed.
- Version notes: Add comments or descriptions when publishing updates, so users know what has changed.
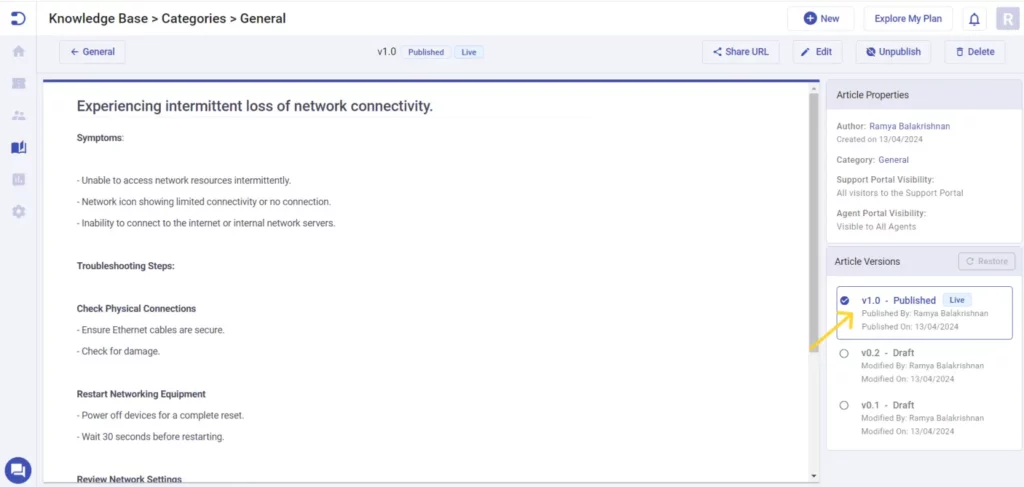
3. Sharing URLs
The ability to generate a shareable link for an article makes collaboration and communication seamless. It improves accessibility for users, reduces repetitive questions by allowing quick sharing of resources. Make sure the URLs are customizable and trackable for better usability and analytics.
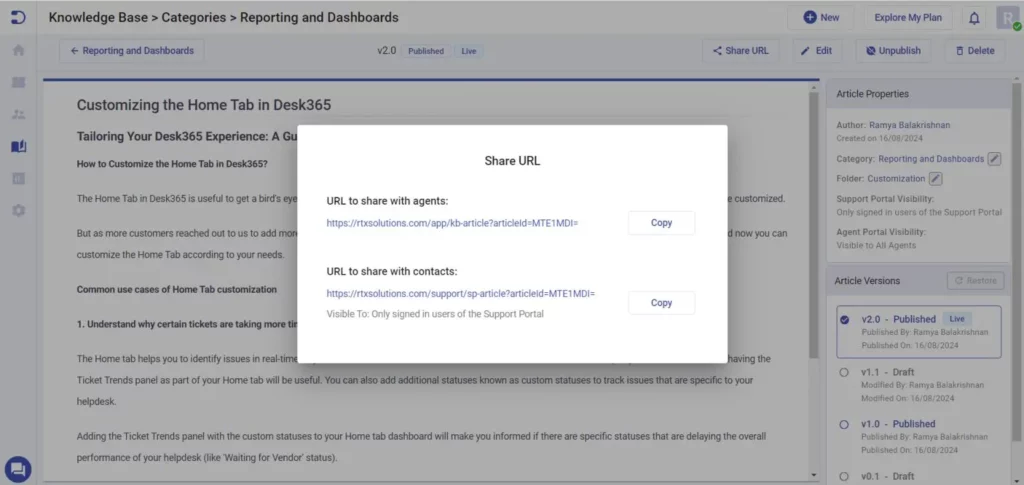
4. Publishing and drafting articles
Not all content is ready to be published immediately, and some articles might need further review before they go live.
Features to include:
- Draft mode: Save articles in draft format while they are being created or reviewed.
- Publish option: Instantly make an article live when it’s ready.
- Status indicators: Clearly label articles as “Draft,” “Published,” or “Under Review.”
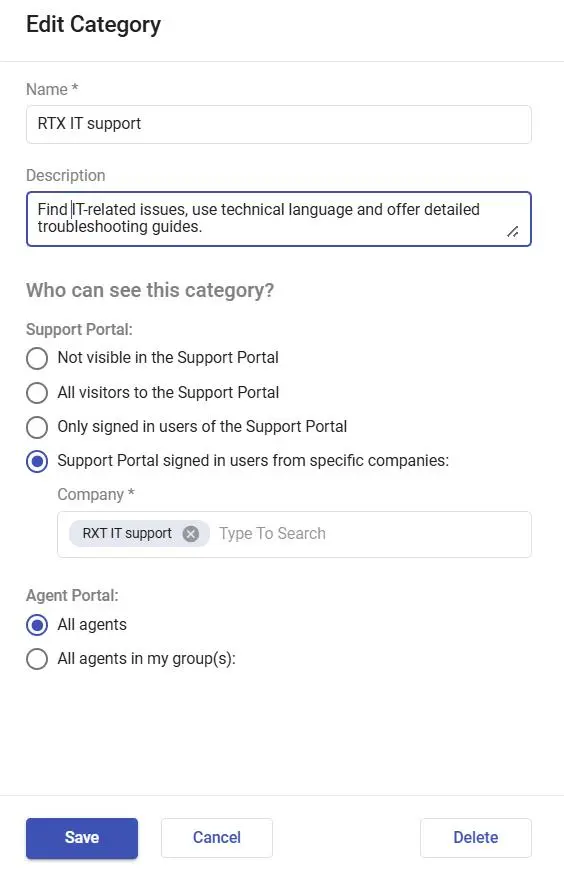
5. Configurable visibility settings
Not every article should be accessible to all users. Configurable visibility settings give administrators control over who can view specific content based on their role or access level.
6. Search functionality with filters
A powerful search tool is crucial for any knowledge base. Pair it with filters such as categories, tags, and access levels to make finding information quick and efficient.
Features to include:
- Keyword search: Allow users to search by specific words or phrases.
- Filter by category or tag: Narrow results based on relevant topics.
- Search suggestion: Provide auto-suggestions based on popular queries.
7. User feedback and analytics
Understanding how your knowledge base is being used can help you improve it.
Features to include:
- Article ratings: Allow users to rate articles for usefulness.
- Comments section: Enable feedback or suggestions directly on articles.
- Usage analytics: Track which articles are most accessed, search terms used, and bounce rates.
How to create an internal knowledge base
Creating an effective internal knowledge base is a key component of a robust knowledge management strategy. It requires careful planning, execution, and continuous improvement. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you build a knowledge base that becomes a valuable resource for your organization.
1. Define your goals
Defining your goals is the first and most crucial step in building an effective internal knowledge base. You need to have a clear understanding of what you aim to achieve and how it will address the specific needs of your organization. Engage with employees to identify gaps in how information is currently shared and accessed.
- Survey employees: Send out surveys to gather input on the current gaps in information-sharing processes.
– What tools do they currently use?
– Are there any bottlenecks in accessing critical information?
- Analyze current practices: Review how your organization currently stores and distributes information.
- Set clear objectives: Based on feedback and observations, define clear and measurable goals, such as:
– Reducing time spent searching for information.
– Improving onboarding processes.
– Streamlining inter-departmental communication.
2. Create a strong team
Next, assembling a dedicated team to create and manage the knowledge base is vital for its success. Building a knowledge base involves multiple tasks such as researching, writing, reviewing, and organizing content. Assign specific roles to team members to ensure accuracy and quality throughout the process. Here are a few roles to include in your team:
- Researchers: Gather accurate and relevant information from various sources.
- Content writers: Create well-written, concise, and user-friendly articles.
- Editors/reviewers: Ensure the content meets quality standards, is error-free, and aligns with the organization’s tone and guidelines.
- Knowledge managers: Oversee the entire knowledge base, ensuring it remains organized, updated, and effective over time.
A strong team will not only help with the initial creation of the knowledge base but will also ensure its long-term sustainability by keeping content relevant and updated.
3. Set up content guidelines
Establishing content guidelines ensures consistency across all articles in the knowledge base. Clear guidelines help maintain a uniform tone, format, and style throughout the content. These guidelines should include templates for articles, standardized navigation structures, and rules for using visuals like images, videos, and infographics. This not only makes the knowledge base professional and appealing but also helps users navigate through the content seamlessly.
Key elements of content guidelines:
- Templates: Use a standardized format for all articles, including the title, introduction, step-by-step instructions, visuals (images, videos, or GIFs), FAQs, or related links
- Navigation structure: Create a user-friendly homepage and a detailed table of contents for easy browsing.
- Formatting rules: Use a consistent font size and style, clear headings and subheadings, and use of bullet points and numbered lists for readability.
- Multimedia: Include visuals to make articles more engaging and easier to understand.
4. Use data and AI to identify topics
Incorporating data and AI into the process can significantly improve the efficiency of creating and maintaining your knowledge base. AI tools can analyze support tickets, identify common issues, and suggest topics that need to be covered. These tools can also assist in automating the drafting of articles and updating outdated content. Leveraging AI allows your team to focus on refining content to make it more effective and user-friendly.
5. Tailor content to your audience
Tailoring content to suit your audience is another essential step in building a successful knowledge base. Different departments, roles, or regions may have unique needs and preferences. Customizing content for specific teams or locations ensures that the knowledge base remains relevant and useful. For organizations operating in multiple regions, offering localized content can enhance accessibility and engagement, creating a personalized experience for every user.
6. Organize content effectively
Organizing content effectively is the backbone of a functional knowledge base. A well-structured knowledge base allows users to quickly find what they need without confusion. It enhances navigation and ensures users can access the right content at the right time.
How to organize content:
- Categories and subcategories:Organize by department, role, or common topics (e.g., “FAQs,” “Policies,” “Troubleshooting Guides”).
- Folders and tags: Use folders for broad topics and tags for specific details to make searching easier.
- Configure visibility: Restrict access based on user roles. For example:
– Support Portal: Limit visibility to signed-in users or specific companies.
– Agent Portal: Restrict content to agents or specific agent groups.
7. Manage and update content regularly
Finally, managing and updating the knowledge base regularly is critical to keeping it relevant and reliable. Analyzing usage metrics and gathering feedback from users can help identify outdated articles and content gaps. Regularly reviewing and revising the knowledge base ensures that it evolves with your organization’s changing needs and trends. This proactive approach builds trust among users and ensures that they always have access to accurate and up-to-date information.
Best internal knowledge base software in 2025
In 2025, several internal knowledge base software solutions stand out for their features and user satisfaction. Here’s an overview of five notable options:
1. Desk365
Desk365 is a comprehensive helpdesk platform that seamlessly integrates with Microsoft Teams, enhancing customer support operations. Its knowledge base feature is designed to facilitate both internal and external information sharing. Here’s a comprehensive look at its features and capabilities.
Key features:
- Multi-brand knowledge base – Desk365’s multi-brand knowledge base enables businesses to create separate repositories for different brands or products under one platform. This feature is particularly beneficial for organizations managing diverse customer segments. With it, businesses can:
– Offer brand-specific or product-specific support articles.
– Tailor solutions to address the unique needs of each customer base.
– Restrict access to content ensuring targeted information delivery.
For instance, a company managing IT and HR support wings can maintain separate knowledge bases, streamlining navigation and improving user experience.
- WYSIWYG editor: Desk365’s What-You-See-Is-What-You-Get (WYSIWYG) editor allows users to create, format, and customize content easily. It supports Markdown and HTML, making it ideal for crafting how-to guides, FAQs, and troubleshooting articles.
- Drag-and-drop organization: This feature simplifies arranging articles, folders, and categories, ensuring effortless management of the knowledge base structure.
- Tables and multimedia support: Users can enhance articles by embedding images, GIFs, or constructing tables directly within the content.
- Instant search: Customers can quickly locate relevant articles through advanced search functionality, reducing wait times and improving efficiency.
- Instant sharing: Articles can be easily shared with agents and contacts, extending their reach.
- Content workflow: Desk365 ensures systematic creation, drafting, and publishing of content, maintaining consistency and quality across the knowledge base.
- Version control: Desk365 tracks changes made to articles, enabling users to view and restore previous versions. This ensures accuracy and prevents loss of valuable information.
- Feedback collection: Desk365’s feedback collection on articles ensures continuous improvement and better user experiences.
- Access settings: Organizations can manage visibility by restricting articles to specific users, agents, companies, or customer groups. This feature ensures sensitive or proprietary information is accessible only to authorized personnel.
What do customers say?
Customers praise the knowledge base feature for being highly effective, particularly highlighting its strong integration with Teams, which enhances user interaction significantly. The search functionality is efficient, and the knowledge base is described as more than adequate for addressing user needs. Additionally, customers value the platform’s active development, with regular feature updates ensuring continuous improvement.
“Teams integration is fantastic and has improved user interaction by at least 500%. Tech team is notified in Teams when tickets come in. Users see tech questions and comments in their teams. Automation features are great. Knowledgebase is more than adequate and search functions work well. Product is actively developed with new features rolling out regularly.”
Source: Capterra
Desk365’s knowledge base feature makes it a versatile solution for organizations aiming to enhance their internal knowledge management and customer support capabilities. Transform your support operations by offering a knowledge base that’s not just functional but truly exceptional. Start your free trial today or request a demo to explore how Desk365 can empower your self-service support strategy.
Omni-Channel
- Microsoft Teams Ticketing
- Email Ticketing
- Customer Support Portal
- Web Form/Web Widget
- Unified Inbox
Process Automation
- Automation Rules
- Custom Response Templates
- Canned Responses
- Tasks/To-do Lists
- Time Tracking
- SLA Management & Business Hours
- SLA Reminders & Escalations
- Multiple SLAs
- SLAs in Automations
Ticket Management
- Custom Ticket Views
- Customer Management
- Responsive Mobile Web Apps
- Multiple Emails
- Multiple Groups/Departments
- Draft with AI
- Collision Detection
- Closure Rules
- Knowledge Base
Data & Analytics
- Customer Surveys & Reports
- Ticket Trend Reports
- Productivity/SLA Reports
- Export Data
- Import Data
Customization
- Custom Email Servers
- Custom Ticket Fields
- Custom Forms
- Custom Roles
- Custom Reports & Graphs
- Remove Desk365 Branding
Integrations
- Entra ID Single Sign-on
- API Access
- Web-hooks
- Power Automate Connector
- Microsoft 365 Copilot Plugin
Support
- Free Setup and Installation
- Priority Support
Start Building Your Internal Knowledge Base Today!
2. Document360
Document360 is an advanced AI-powered knowledge base software designed for creating both public and private knowledge bases. Its intuitive design and feature-rich environment make it an excellent choice for businesses aiming to centralize and streamline their documentation processes. This platform caters to various use cases, from internal employee resources to external customer support documentation.
Key features
- AI Integration: Document360 leverages AI to assist with content creation and organization, helping teams generate relevant topics and manage knowledge efficiently.
- Rich text editing: The editor supports detailed formatting, multimedia embedding, and markdown, offering flexibility in content creation.
- Version control: Tracks changes made to articles, enabling users to roll back to previous versions if needed.
- Advanced search: Customers can quickly find the information they need through a robust and intuitive search function.
- Multilingual support: Ideal for global businesses, as it allows content creation in multiple languages.
Pros & cons of Document360
Pros
- Users appreciate the clean and intuitive design, which simplifies the process of creating and managing content.
- The incorporation of AI assists in content creation and management, enhancing efficiency.
- Suitable for both internal and external knowledge bases, providing flexibility for various organizational needs.
Cons
- Some users find the pricing model to be on the higher side, especially for smaller teams.
- A few customers have noted limitations in customization options for the knowledge base portal.
What do customers say?
On platforms like G2 and Capterra, customers commend Document360 for its clean interface, which simplifies onboarding and content management. Many users highlight its dual suitability for internal and external knowledge bases. However, some note that its pricing structure might be restrictive for smaller teams. Additionally, while the platform offers significant capabilities, users have occasionally mentioned limited customization options for portal design.
“Pricing is quite expensive, even annualised. Otherwise, we don’t have any significant complaints. It’s met our needs well.”
Source: G2
“One potential drawback of Document 360 is that it may lack some advanced customization options. While it provides basic customization features, users with more specific or complex requirements may find limitations in tailoring the software to their exact needs. However, this may vary depending on individual use cases and preferences.”
Source: Capterra
3. Confluence
Confluence by Atlassian is a dynamic and scalable knowledge management tool, particularly popular among large enterprises and tech-driven organizations. Known for its seamless integration with other Atlassian products, it serves as a comprehensive hub for collaboration, documentation, and knowledge sharing
Key features
- Integration with Atlassian suite: Works seamlessly with tools like Jira, enabling smooth workflows for teams in project management and software development.
- Customizable templates: Offers pre-built templates to standardize and expedite the content creation process.
- Collaboration tools: Teams can work together on documents, leave comments, and track changes in real time.
- Permission management: Ensures secure access by enabling administrators to assign user roles and content visibility.
Pros & cons of Confluence
Pros
- Seamless integration with other Atlassian products like Jira enhances project management capabilities.
- Offers robust tools for creating detailed and structured documents, including support for multimedia content.
- Designed to accommodate the needs of large organizations with extensive documentation requirements.
Cons
- New users may find the platform complex and may require time to learn and adapt.
- Some users have reported performance slowdowns with large datasets.
What do customers say?
Customers highlight the platform’s strong integration capabilities and its effectiveness as an enterprise-level solution, especially for creating detailed and structured documentation. It is widely appreciated for its utility in large-scale operations. However, users point out a steep learning curve and note that the platform’s complexity often requires additional training and IT involvement for certain tasks, such as managing access. Concerns about search functionality and performance issues with large datasets have also been raised, making it less ideal for smaller businesses. Some find it costly and challenging for smaller teams to adopt effectively.
“It is a bit pricey and difficult to be used by small corporates. We find it difficult.”
Source: G2
“It takes a bit of a learning curve to get used to where you find everything. Additionally, granting access to people on different pages is challenging – to the point that it seems like we have to include IT in those type of requests – which shouldn’t be the case, and is MUCH easier to do in Quip. The search functionality can also leave some things to be desired, as many times it takes 4-5 searches to finally find what you’re looking for.”
Source: Capterra
4. Nuclino
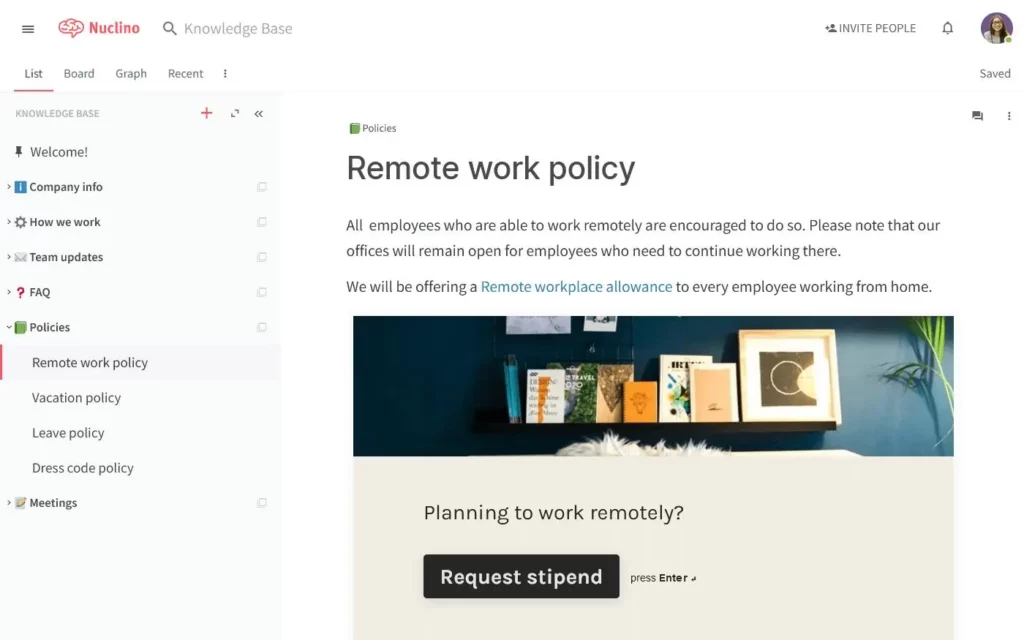
Nuclino is a knowledge base platform designed mainly for internal use, providing teams with a fast and seamless way to collaborate and share knowledge. It enables the creation of documents and project management within a unified workspace. It emphasizes simplicity and speed, making it a preferred choice for small to medium-sized teams seeking a straightforward knowledge base solution.
Key features
- Real-time collaboration: Teams can edit and view changes instantly, fostering efficient communication and collaboration.
- Unified workspace: Combines document creation, knowledge sharing, and project management in one platform.
- Integration support: Connects with popular tools like Slack, Google Drive, and Trello, enhancing team workflows.
- Graph view: Provides a visual representation of content relationships, helping teams navigate interconnected documents easily.
Pros & cons of Nuclino
Pros
- Teams can collaborate in real-time, with instant updates and changes visible to all members.
- The user-friendly design makes it easy for teams to adopt and start using without extensive training.
- Nuclino integrates with various tools, enhancing workflow efficiency.
Cons
- May lack some advanced functionalities required by larger organizations.
- Customization options are somewhat limited compared to other platforms.
What do customers say?
Nuclino scores 4.7/5 on G2, with users praising its ease of use, intuitive design, and real-time collaboration features that enhance team dynamics. However, some users note limitations, such as the search functionality, which does not account for typos, leading to zero results if a query is misspelled. Additionally, the platform’s pricing model has been highlighted as a drawback, with customers expressing the need for a more affordable tier for non-editing users who primarily require read-only access to articles.
“The search does not handle typos. It will show zero results if you mistype.”
Source: G2
“A cheaper tier for non-editing users would be appreciated, as some of our team interfaces with the articles in a read-only capacity.”
Source: Capterra
5. Guru
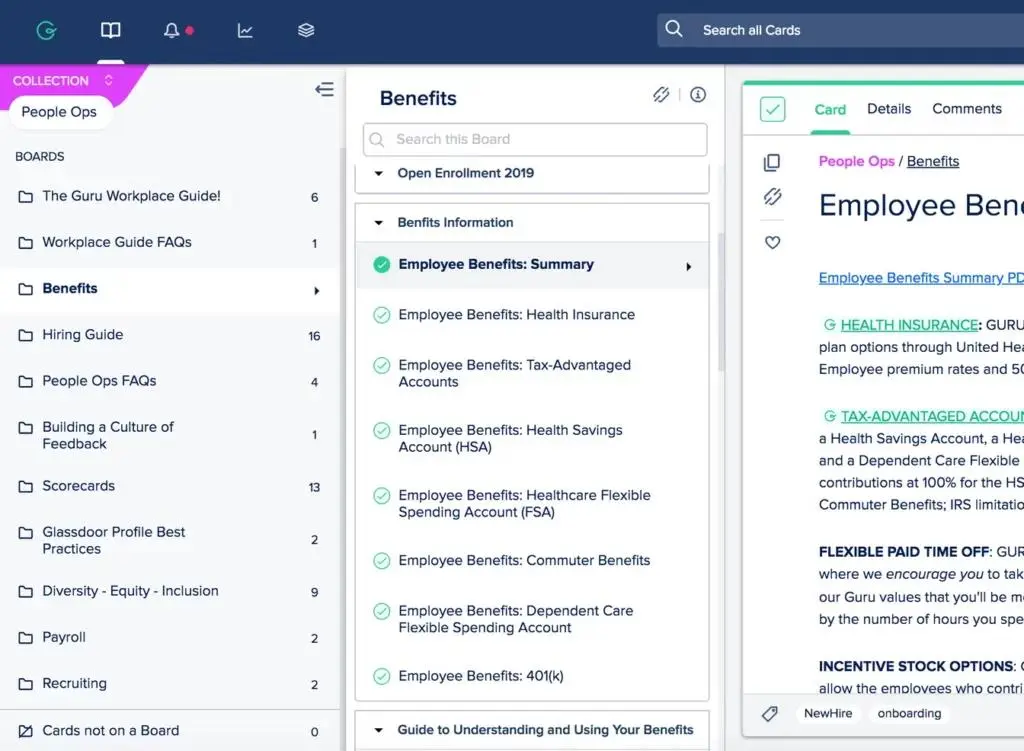
Guru is an AI-driven platform popular for internal knowledge management across teams, offering advanced customizations and integrations with various tools. It serves as a centralized repository for organizational knowledge, enhancing team collaboration.
Key features
- AI-powered knowledge management: Suggests relevant content based on user needs, streamlining information retrieval.
- Browser extension: Allows users to access information without leaving their current workflow, enhancing productivity.
- Knowledge verification workflow: Ensures content accuracy by prompting regular verification of information.
- Slack and Microsoft Teams integration: Offers seamless integration with popular communication tools, making it a natural extension of daily workflows.
Pros & cons of Guru
Pros
- Leverages AI to provide relevant information and suggestions, improving productivity.
- Ensures information accuracy through regular verification prompts
Cons
- Some users report a learning curve associated with fully utilizing all features.
- The cost may be a consideration for smaller teams or startups.
What do customers say?
Customers appreciate Guru’s user-friendly interface and browser extension, which streamline the process of centralizing and accessing relevant information within existing workflows. Many users commend its ability to enhance productivity by integrating seamlessly into their daily tasks. However, some areas for improvement have been noted. The search functionality can be limiting, as it requires exact matches to retrieve articles. Additionally, users have reported occasional platform lag when dealing with a large volume of Guru Cards, suggesting the need for better content prioritization to maintain performance and responsiveness.
“It’s not a dislike but room for improvement I guess, sometimes articles are not showing up when I search for keywords and it has to be the exact article page.”
Source: Capterra
“There isn’t much I dislike about Guru, but I have noticed that the platform can sometimes lag when there’s an overload of Guru Cards. It would be great if the platform could streamline or prioritize content when there’s a large volume of information, to maintain its usual speed and responsiveness.”
Source: G2
Here's a Powerful Solution for Your Internal Knowledge Base!
Desk365’s robust internal knowledge base feature helps your team centralize information, collaborate seamlessly, and stay organized. With version control, category-level access, and intuitive search capabilities, it’s the perfect tool for creating a knowledge hub that fuels productivity.
Building an internal knowledge base is simple and easy, with the right tools and strategies, With a powerful tool it becomes an invaluable asset for your organization. Start today and see the difference it makes in your team’s productivity and your customers’ satisfaction!
Frequently asked questions
An internal knowledge base is a centralized repository of information, resources, and guides designed to help team members access critical data efficiently, improving collaboration and productivity.
Desk365 offers a user-friendly interface, robust customization options, and advanced features like category-level access and version control, making it perfect for creating and managing an internal knowledge base tailored to your organization’s needs.
Yes, Desk365’s multi-brand knowledge base feature allows you to create separate repositories for different brands, products, or departments, ensuring organized and relevant content for each audience.
It’s recommended to update your knowledge base regularly to ensure accuracy and relevance. Review and revise content as your products, services, or processes evolve.